I explained the machine learning in the edge device has a huge potential in the previous post. Running ML algorithm in edge device will provide a nice experience of interactive application and can protect data privacy by keeping the data in the local device.
I find another approach to achieve the purpose. That is Federated Learning.
Federated learning is a technology to allow us to train a machine learning model in the local device without losing the chance to improve the model globally. As it is not necessary to connect to the internet and send the log data to the server in order to train the model, that is consistent with the policy I mentioned previously. Here is the rough diagram showing how federated learning works.
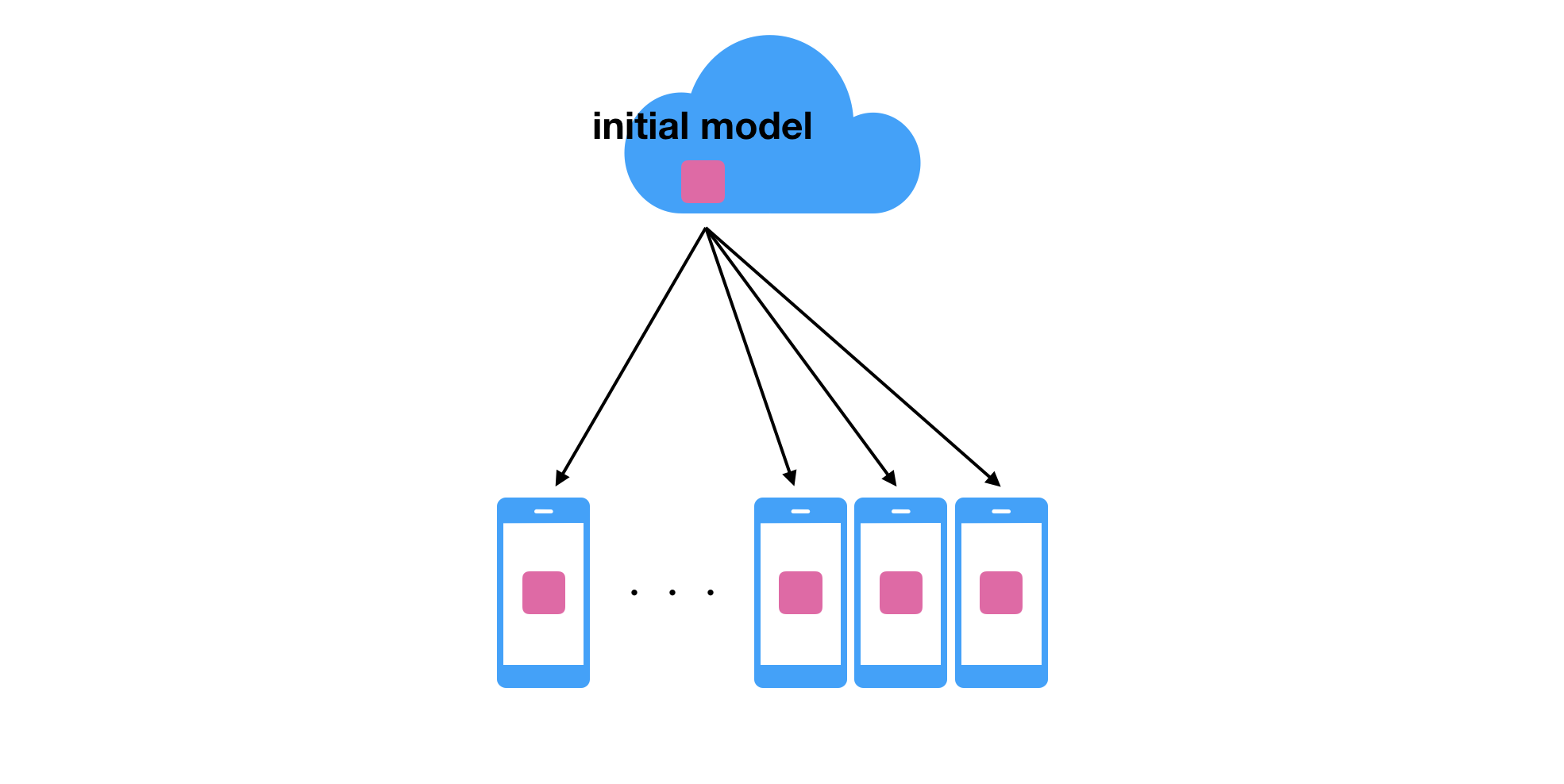
First, the initial model is distributed to the edge devices. That model is trained with the general dataset so it’s not optimized personally. We need to train the model based on the user data without sending it to the server side. Federated learning comes here. The model training happens in the client side based on the data generated by the user. After the training, only the updated model will be sent to the server side which does not need to include any actual data based on the user behavior.
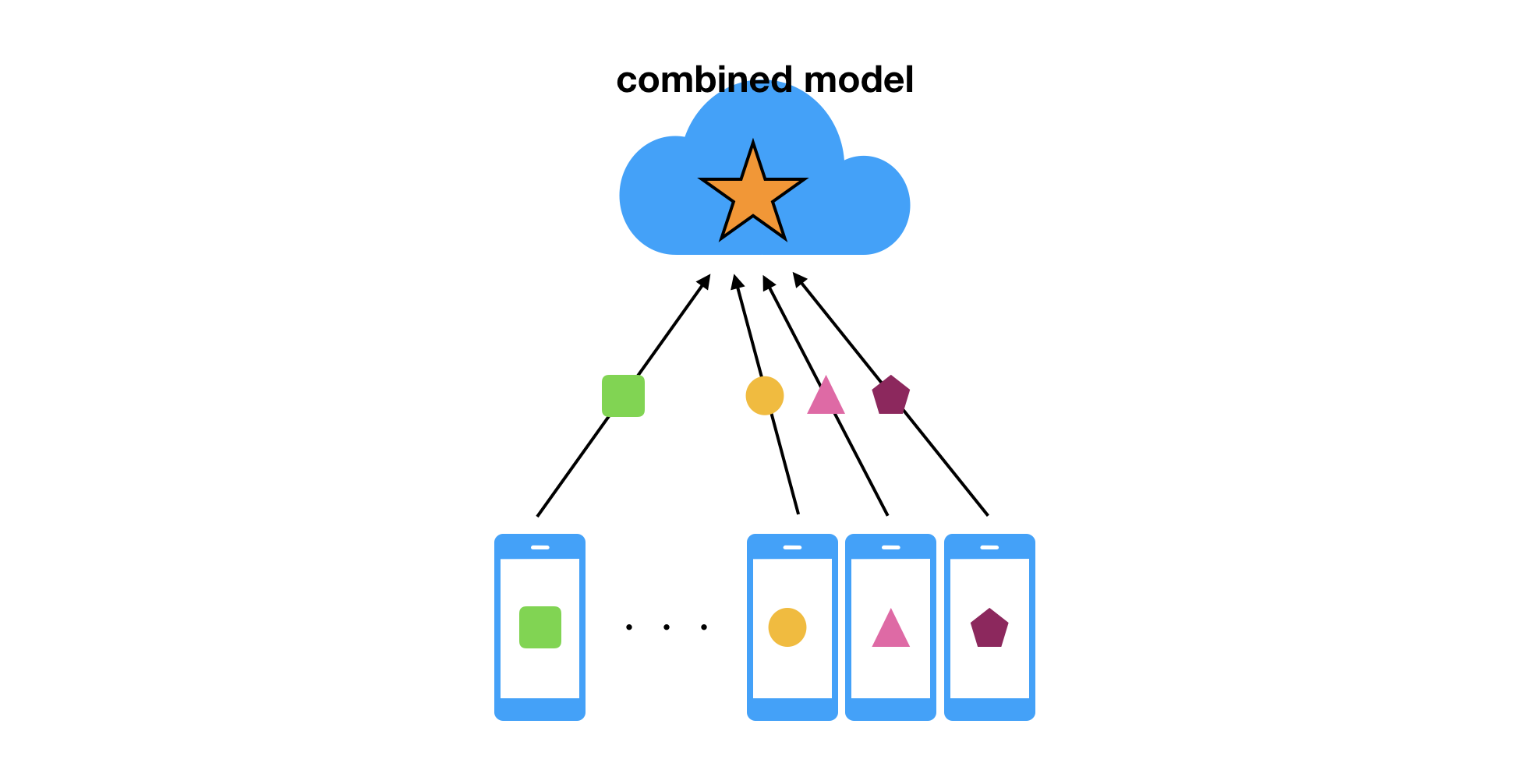
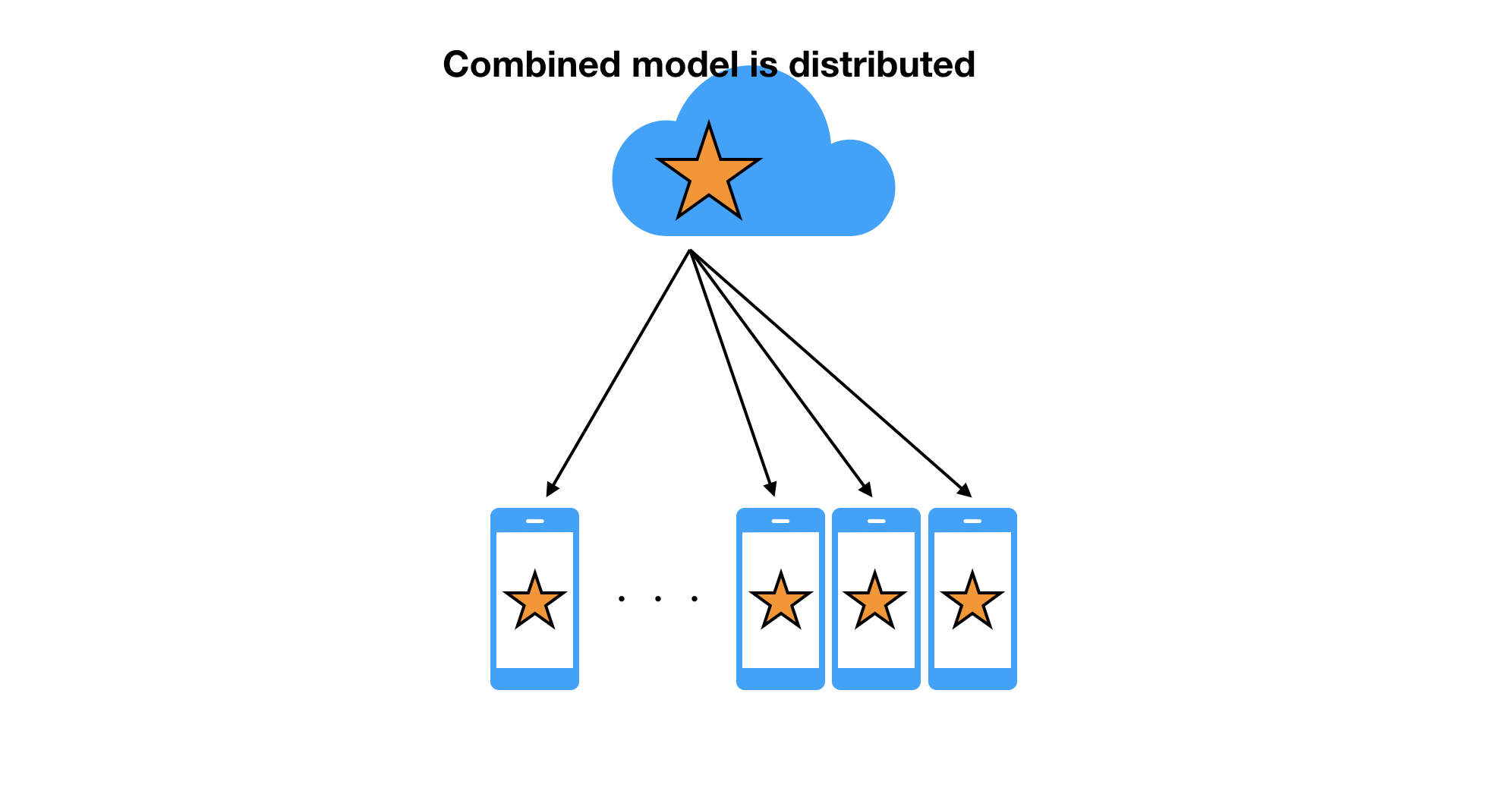
The training can happen in a local device so that we can minimize the latency caused by the network. After a while, the new model is created on the server side. That will be distributed to all client devices so that each user can receive the benefit of the training based on the various kind of data.
TensorFlow Federated is a framework to do federated learning by using TensorFlow. TensorFlow Federated can update Keras model in a federated learning manner. That means you can easily integrate your own Keras model with TensorFlow Federated. The following code shows a simple example of how the model is updated by using TensorFlow Federated.
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_federated as tff
# Wrap a Keras model for use with TFF.
def model_fn():
return tff.learning.from_compiled_keras_model(
mnist.create_simple_keras_model(), sample_batch)
# trainer defines the policy how to combine the multiple models obtained from clients.
trainer = tff.learning.build_federated_averaging_process(model_fn)
state = trainer.initialize()
for _ in range(5):
state, metrics = trainer.next(state, train_data)
print (metrics.loss)
Although TensorFlow Federated seems to be experimental, I believe it has the potential to enable us to train a huge machine learning model efficiently and safely. Please take a look into the above video for more detail. The talk was spoken at the TensorFlow Dev Summit held in Sunnyvale, CA at Mar 6-7th. The following post also provides you other interesting topics announced in the conference. Thanks!